Week 3 - XPATH
Table of content
- Review Week2 Tutorial
- Look at some aspects of XML
- Namespaces
- Data Models
- Introduce XPath
- Look at some common XPath syntax
Namespaces
- Allow us to group elements and attributes under a common heading.
- Namespaces are not parts of the XML specifications, but they are widely supported.
Namespaces Declarations
xml
<outerElement xmlns:events="URL" xmlns:graphics="URL">- You can now use 'events' and 'graphics' prefixes:
xml
<events:title>Content</events:title>and
xml
<graphics:title>Content</graphics:title>- URL example: https://www.cdut.edu.cn/nm/week3
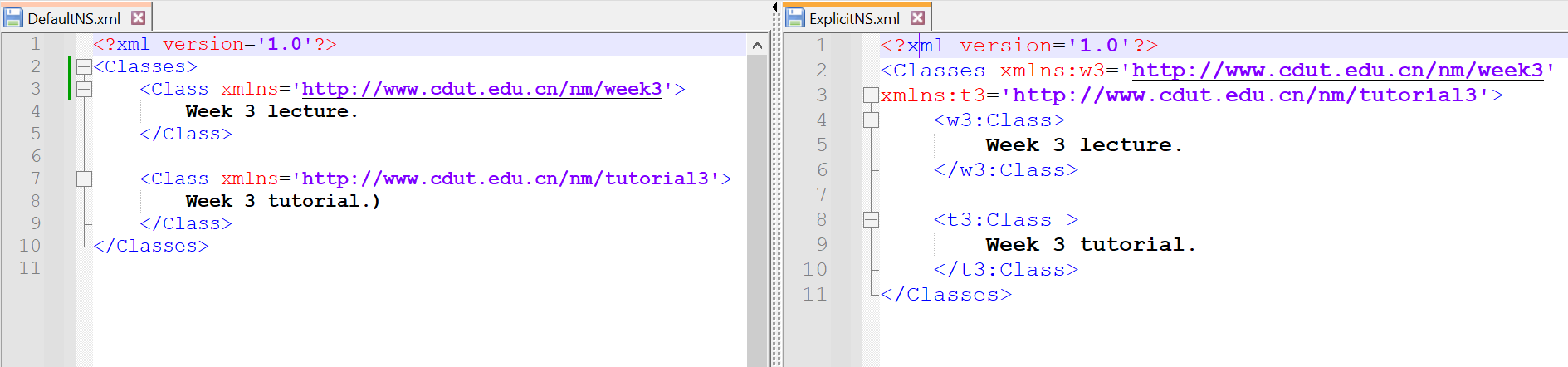
Namespaces Types
| Default | Explicit |
|---|---|
| - No prefix - Namespace applies to every unqualified tag (a tag without a prefix). | - Utilizes a prefix. - Shorthand notation for the namespace. |
DOM
- Document Object Model (DOM):
- Originally developed for HTML. Supported by most browsers.
- Represents the content of the XML or HTML document as a tree structure.
- Using DOM, we can easily read and update the contents of the document.

- Online DOM viewer: https://software.hixie.ch/utilities/js/live-dom-viewer/
XPATH
- What is Xpath?
- Allows us to use path expressions to navigate an XML document.
- It allows us to select only the nodes we're interested in.
- So its:
- Expression language.
- Contains some standard functions.
- Non-XML.
- XSLT relies heavily on the use of XPath to navigate a document, and find relevant nodes.
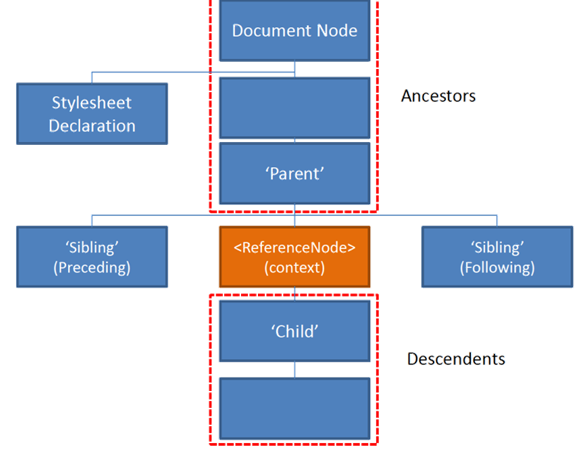
XPATH Tree Structure
- Xpath works on the following kinds of nodes
TIP
sibling: <正式>兄弟姐妹
Using XPATH
- Xpath works on the following kinds of nodes
Xpath paths (Absolute vs Relative)
| Absolute Location Path | Relative Location Path |
|---|---|
| - If your location path starts with the root node or a forward slash (/) you are using an absolute location path - e.g. /bookstore/book[2]/author | - If your location path begins with the name of a descendant, you're using a relative location path. - Less complex than the absolute path. - e.g. //*/book[2]/author |
Xpath tools online
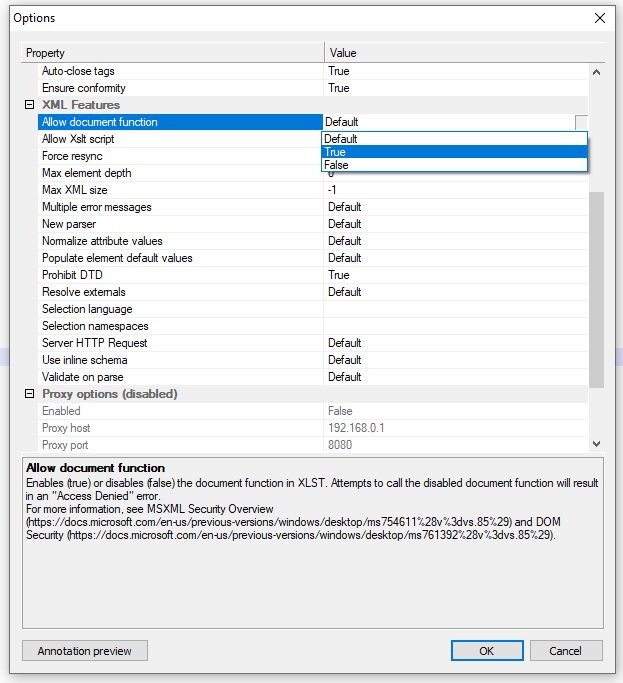
Preparing Notpad++
Some key XPath expressions
- Xpath works on the following kinds of nodes
| Expression | Description |
|---|---|
| nodename | Selects all nodes with the name "nodename" |
| / | Selects from the root node |
| // | Selects nodes in the document from the current node that match the selection no matter where they are |
| . | Selects the value of the current node |
| .. | Selects the parent of the current node |
| @ | Selects attributes |
NOTE
* 也作通配符,但会把所有元素一个一个地单列输出
XPath Examples
| Path Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| bookstore | Selects all nodes with the name "bookstore" |
| /bookstore | Selects the root element bookstore **Note:**If the path starts with a slash ( / ) it always represents an absolute path to an element! |
| bookstore/book | Selects all book elements that are children of bookstore |
| //book | Selects all book elements no matter where they are in the document |
| bookstore//book | Selects all book elements that are descendant of the bookstore element, no matter where they are under the bookstore element |
| //@lang | Selects all attributes that are named lang |
Namespaces Xpath Examples
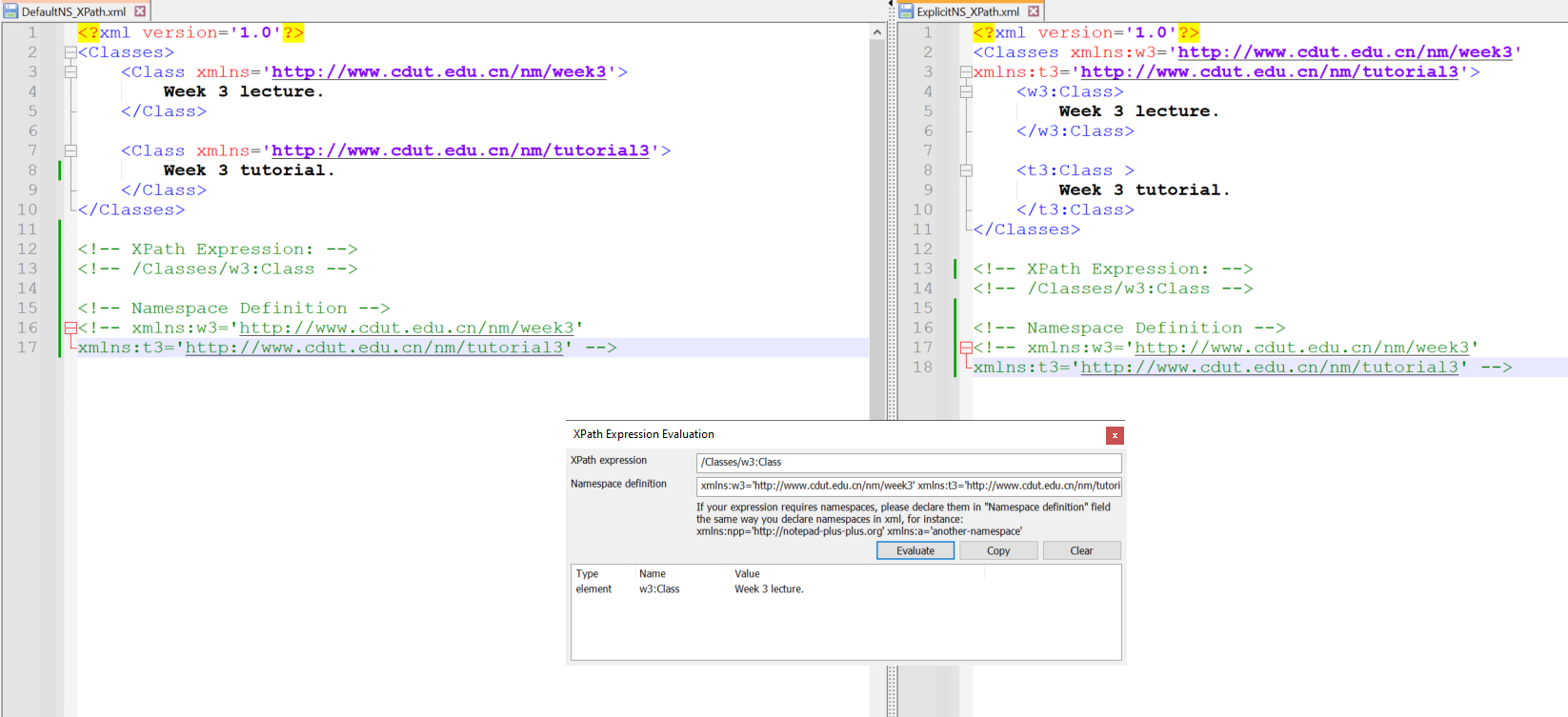
Predicates
Predicates examples
| Path Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| /bookstore/book[1] | Selects the first book element that is the child of the bookstore element. |
| /bookstore/book[last()] | Selects the last book element that is the child of the bookstore element |
| /bookstore/book[last()-1] | Selects the last but one book element that is the child of the bookstore element |
| /bookstore/book[position()❤️] | Selects the first two book elements that are children of the bookstore element |
| //title[@lang] | Selects all the title elements that have an attribute named lang |
| //title[@lang='en'] | Selects all the title elements that have a "lang" attribute with a value of "en" |
| /bookstore/book[price>35.00] | Selects all the book elements of the bookstore element that have a price element with a value greater than 35.00 |
| /bookstore/book[price>35.00]/title | Selects all the title elements of the book elements of the bookstore element that have a price element with a value greater than 35.00 |
Other Examples://Actor [@gender='male’]//Movie[2]/Top_Cast/Actor[@gender='male’]//Movie[2]/Top_Cast/Actor[last()]/.//Actress[text()='Takayo Fischer’]/Movies/Movie[2]/Top_Cast/Actress [@gender='female'][last()-1]
XPATH Axes
- An Axes represents a relationship to the current node on the tree.
| AxisName | Result |
|---|---|
| ancestor | Selects all ancestors (parent, grandparent, etc.) of the current node |
| ancestor-or-self | Selects all ancestors (parent, grandparent, etc.) of the current node and the current node itself |
| attribute | Selects all attributes of the current node |
| child | Selects all children of the current node |
| descendant | Selects all descendants (children, grandchildren, etc.) of the current node |
| descendant-or-self | Selects all descendants (children, grandchildren, etc.) of the current node and the current node itself |
| following | Selects everything in the document after the closing tag of the current node |
| following-sibling | Selects all siblings after the current node |
| namespace | Selects all namespace nodes of the current node |
| parent | Selects the parent of the current node |
| preceding | Selects all nodes that appear before the current node in the document, except ancestors, attribute nodes and namespace nodes |
| preceding-sibling | Selects all siblings before the current node |
| self | Selects the current node |
XPATH Axes Examples
| AxisName | Example |
|---|---|
| ancestor | //Actor/ancestor:😗 |
| ancestor-or-self | //Actor/ancestor-or-self:😗 |
| attribute | //Actor/attribute::gender |
| child | //Top_Cast/child::Actor[text()='Will Smith’] //Movie/child:😗 |
| descendant | //Movie/descendant:😗 |
| following-sibling | //Actor [text()='Will Smith']/following-sibling::Actress |
| parent | //Actor [text()='Will Smith']/parent:😗 |
| self | //Actor/self:😗 |